Indications for operation
Frozen shoulder (adhesive capsulitis)
Frozen shoulder (adhesive capsulitis)
All surgical procedures have some element of risk attached.
The risks outlined below are the most common or most significant that have been reported.
Although a full range of motion will be obtained during the procedure some patients experience a relapse and develop a frozen shoulder again.
If an infection does occur it is usually superficial in the wounds and is easily treated with antibiotics.
Rarely the infection can be deep inside the joint and this requires surgery to wash the joint out.
The axillary nerve runs close to the bottom of the joint and, if damaged causes weakness of the deltoid muscle and difficulty in raising the arm.
Considerable forces can be applied during the manipulation and it is possible to break the arm. This is rare and avoidable if care is taken.
General Anaesthetic with an interscalene block (Fully asleep with a local anaesthetic injection into the side of the neck will numb the nerves to the shoulder for post-operative pain relief)
Arthroscopic
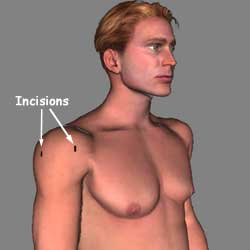
2 ½ cm incisions will be made in the shoulder, one to the back, one at the side and one at the front of the shoulder.
The gleno-humeral (shoulder) joint will be inspected first. The capsule (lining of the joint) will be released to allow the full range of motion to be regained.
Small butterfly paper stitches will be used to close the wounds.
Elastoplast dressings will be placed over the top of the paper stitches and an adhesive bandage over the top of this.
A sling will be placed on the arm and it may feel numb for the rest of the day. You can go home when you feel comfortable and will be given instructions on what to do next.
It is important that physiotherapy is started very soon after the surgery to enable the full benefit to be obtained.